What is Hepatology?
The body is made up of many key systems. Each of these networks plays a vital role in maintaining life-sustaining functions. The study of the entire human body is known as biology. Biology encompasses several sub-categories related to specific bodily regions. One specific sub-category is scientifically classified as hepatology.
Overview
Hepatology is the study of the liver and other digestive system components, such as the pancreas, gallbladder, and bile ducts.
These organs carry out crucial duties, including the secretion of chemicals aiding in digestion, shepherding food through the gastrointestinal tract, and producing and eliminating potentially hazardous waste materials.
Hepatologists
Doctors specializing in hepatology are called hepatologists. These physicians are specially trained to understand the inner workings of these organs, diagnose diseases impacting them, and treat such conditions.
Statistics About Liver and Related Diseases
There is a growing need for specialists as liver and related problems continue to increase in prevalence.
Roughly 2% of the United States adult population lives with some diagnosed liver condition. Additionally, millions worldwide live with diagnosed and undiagnosed hepatic-related ailments.
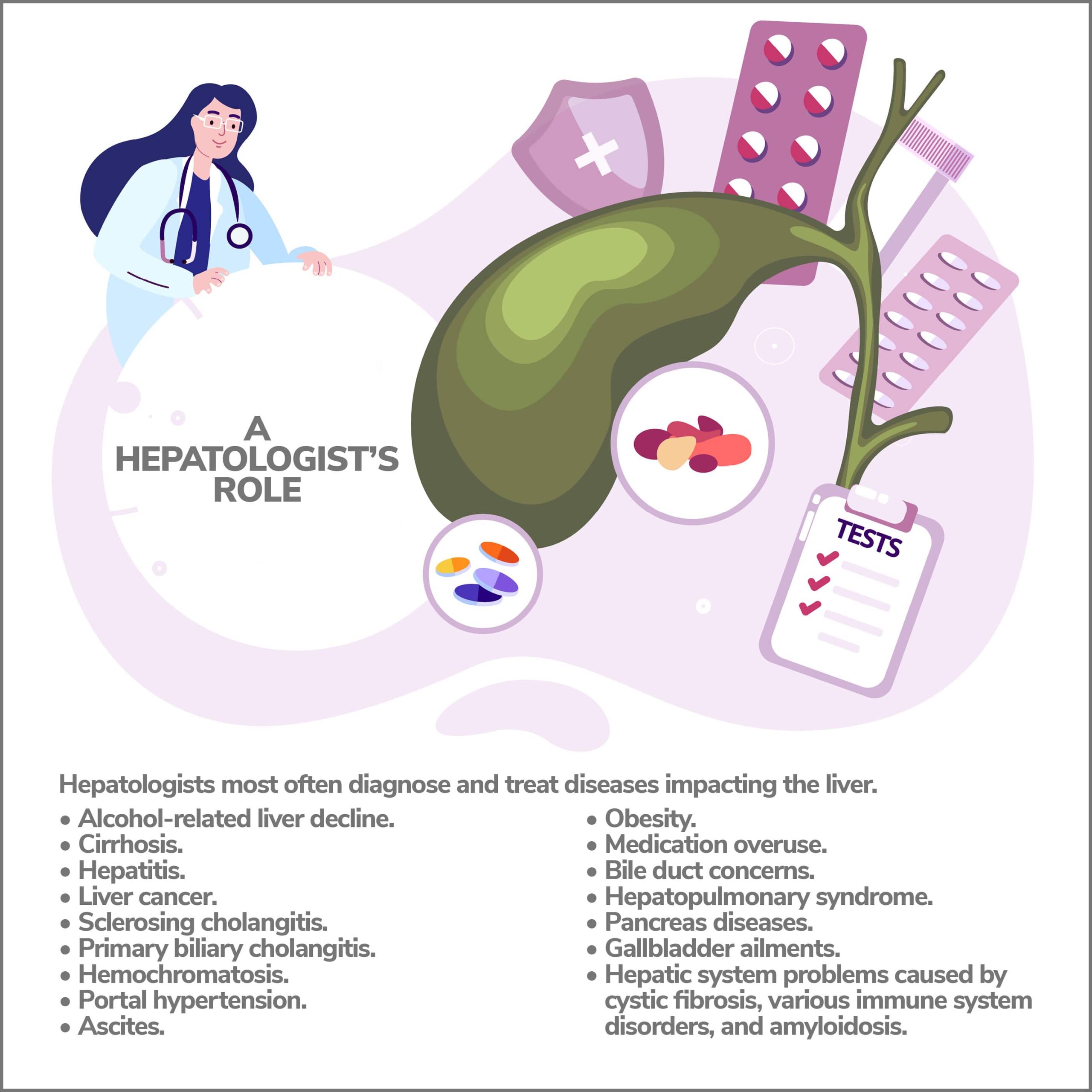
A Hepatologist’s Role
Hepatologists most often diagnose and treat diseases impacting the liver. Notable but relatively common illnesses include alcohol-related liver decline, cirrhosis, hepatitis, and liver cancer.
These specialists identify and treat other conditions, including:
- Sclerosing cholangitis.
- Primary biliary cholangitis.
- Hemochromatosis.
- Portal hypertension.
- Ascites.
- Obesity.
- Medication overuse.
- Bile duct concerns.
- Hepatopulmonary syndrome.
- Pancreas diseases.
- Gallbladder ailments.
Hepatologists also remediate hepatic system problems precipitated by other illnesses like cystic fibrosis, various immune system disorders, and amyloidosis.
Medical Procedures Hepatologists Perform
Hepatologists perform many procedures that help them diagnose specific illnesses, including:
- Imaging Tests – Hepatologists use internal imaging diagnostics like computerized tomography (CT scans) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to capture photos of the liver and other pertinent organs. These images provide insight into the inner workings of the organs and simplify identifying existing abnormalities.
- Biopsies – Hepatic surgeons perform biopsies by removing small amounts of liver, pancreatic, or gallbladder tissue. Once these samples are collected, they are brought to laboratories for further analysis. Biopsies are usually taken from growths like tumors, cysts, or other suspicious masses.
- Endoscopies – During these examinations, doctors insert long, tube-like devices equipped with a camera and surgical tools into your hepatic region. The camera lets hepatologists view an organ, identify obvious irregularities, and render a swifter diagnosis.
- Blood Tests – Hepatology specialists often extract small amounts of blood from patients. These samples are then subjected to various tests. Results often reveal the presence of existing hepatic issues or suggest hepatic system organs are not functioning optimally.
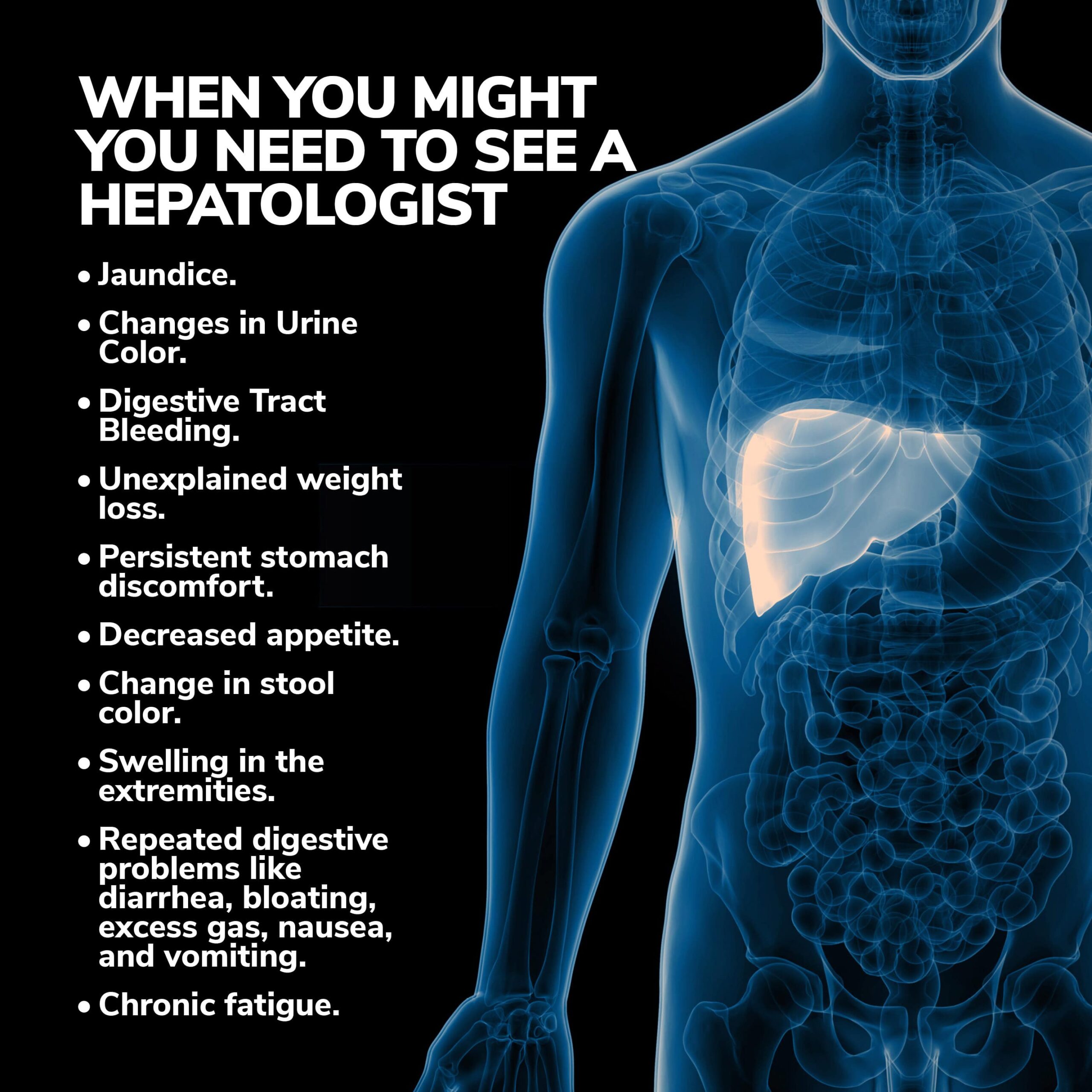
When Might You Need to See a Hepatologist?
You might need a hepatologist if your:
- Liver Test Function Results are Irregular or Unusual – Hepatologists conduct these measurements to determine the effectiveness and strength of your liver proteins and enzymes. When these readings either return too high or low, an underlying liver concern might be the cause.
- Symptoms Suggest Potentially Serious Hepatic Issues – Consultation with a hepatologist is usually recommended when you experience severe liver ailment-related symptoms, including:
- Sudden bleeding in your upper gastrointestinal region may be caused from liver scarring (cirrhosis). This serious and potentially fatal condition usually results from chronic heavy alcohol abuse. Advanced hepatitis cases can also precipitate the illness.
- Experiencing Miscellaneous Symptoms – You might need a hepatologist’s evaluation following the onset of symptoms such as:
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Persistent stomach discomfort.
- Decreased appetite.
- Change in stool color.
- Swelling in the extremities.
- Repeated digestive problems like diarrhea, bloating, excess gas, nausea, and vomiting.
- Chronic fatigue.
Physical symptoms such as an increased heart rate, elevated body temperature, unexplained body aches, and general malaise may also warrant a hepatologist consultation.
The Training a Hepatologist Receives
Hepatologists receive thorough and specialized training. To achieve this title, they must complete several steps, including:
- Medical School – Following graduation from a four-year university or college, prospective hepatologists graduate from an accredited medical school with a Doctor of Medicine degree. These studies usually take four years to complete.
- Residency – After medical school, future hepatologists will complete three years as an internist in residency at a hospital or medical facility.
- Receive Certification as a Gastroenterologist – Hepatology is a sub-specialty of the larger medical branch of gastroenterology. Would-be hepatologists must receive certification from the American Board of Internal Medicine confirming their board certification as a gastroenterologist. Title confirmation is not awarded until candidates pass a stringent examination.
- Fellowship – Future hepatologists then serve a three-year fellowship in the gastroenterology specialty, followed by an advanced fellowship in transplant hepatology. Candidates may also fulfill this requirement by serving a three-year fellowship combining gastroenterology and transplant hepatology.
- Transplant Hepatology Certification – The final step prospective hepatologists must climb is attaining transplant hepatology certification.
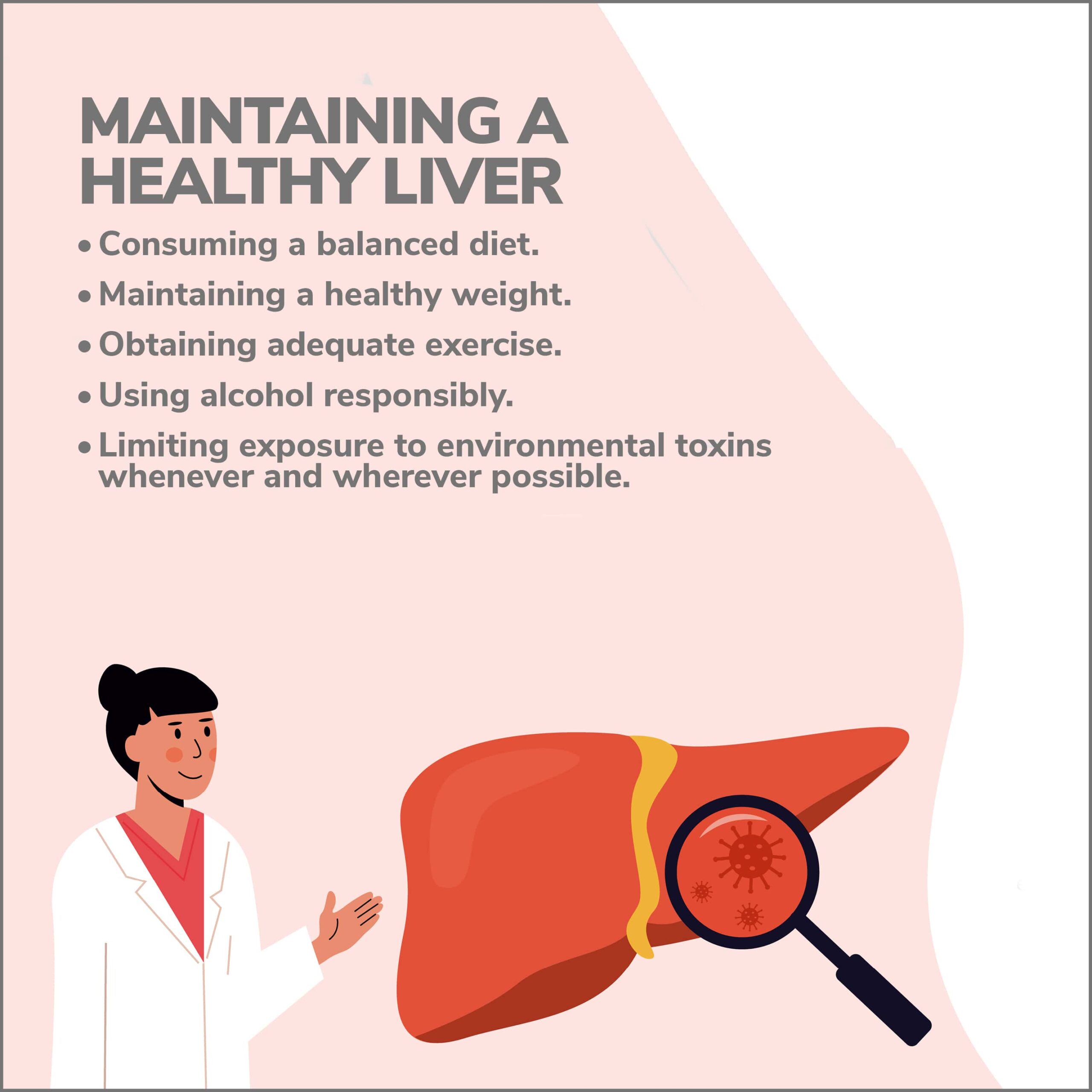
Maintaining A Healthy Liver
Hepatologists are highly skilled and well-trained physicians capable of diagnosing, easing symptoms, or potentially curing various hepatic illnesses. You might avoid the need for treatment from such medical professionals and improve your chances of living a longer and healthier life through liver maintenance practices, including:
- Consuming a balanced diet.
- Maintaining a healthy weight.
- Obtaining adequate exercise.
- Using alcohol responsibly.
- Limiting exposure to environmental toxins whenever and wherever possible.
Air and blood-borne pathogens can adversely impact liver function and ultimately result in various hepatic disorders. You might reduce your risk of exposure to these organisms by not sharing personal items, not reusing needles, washing your hands frequently with warm water and soap, and getting vaccinated against potential dangers like hepatitis.
Exercise caution when using certain over-the-counter and prescription drugs. Some medications take longer for the body to break down and eliminate and may collect inside your liver. When such accumulations occur, they can be harmful to liver structure and function. You are urged to disclose all medications you use with your doctor and take drugs only as directed.
Contact Us
Our practice began more than 15 years ago and has emerged as one of the leading gastroenterology practices in central Florida. We perform a host of diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere where patient care is always a top priority. Contact us today!