
How to Relieve IBS: 5 Expert Tips to Ease Your Symptoms
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common digestive disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s a condition that can have a significant impact on your daily life, but with the right strategies, it is possible to manage the symptoms effectively and live a more comfortable, active life. IBS can manifest in a variety of ways, causing symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal discomfort. Although it can be a long-term challenge, there are many effective ways to control the symptoms and restore balance to your digestive system. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll define what IBS is, explore its common symptoms, and provide actionable tips to help ease your symptoms and improve your digestive health.
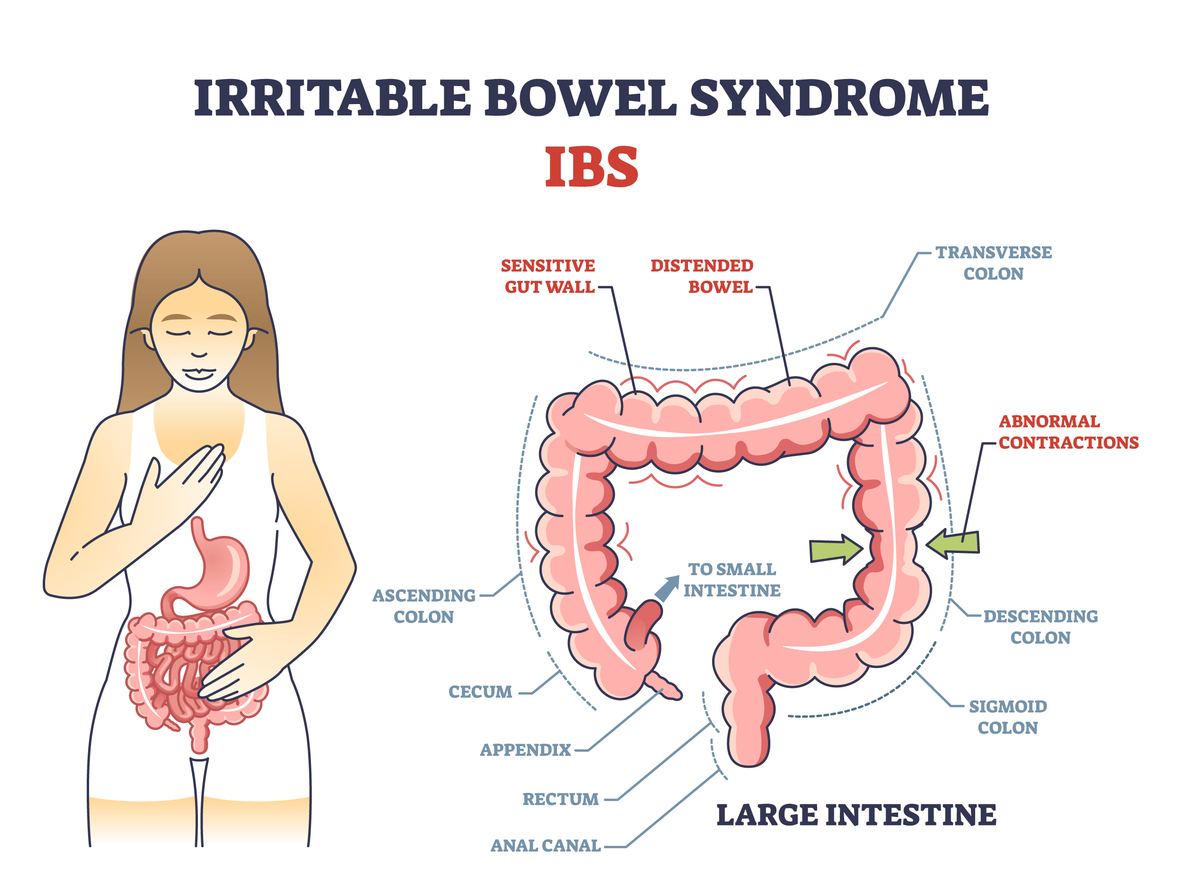
What Is IBS?
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. Unlike diseases that cause visible damage to the digestive system, IBS is characterized by a group of symptoms related to altered bowel function. IBS does not cause permanent damage to the intestines, but it can cause significant discomfort and distress. The exact cause of IBS remains unknown, but it is thought to be linked to several factors, including stress, genetics, gut motility problems, and an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Additionally, IBS can be triggered or worsened by various factors such as certain foods, stress, or hormonal changes. While the condition itself is not life-threatening, it can significantly affect a person’s quality of life, making it essential to explore ways to manage and minimize symptoms.

Common Symptoms of IBS
People with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) experience a range of digestive symptoms that can vary in severity and frequency. While symptoms differ from person to person, the most common ones include:
- Abdominal Pain and Cramping: Discomfort or cramping in the lower abdomen, often relieved after a bowel movement.
- Bloating and Gas: A feeling of fullness and excessive gas, which can cause visible swelling in the stomach.
- Changes in Bowel Movements: Alternating between diarrhea and constipation or experiencing one more frequently.
- Mucus in Stool: Some people with IBS notice clear or white mucus in their bowel movements.
- Urgent Need to Use the Bathroom: A sudden and uncontrollable urge to have a bowel movement, sometimes leading to anxiety in social situations.
5 Tips to Ease IBS Symptoms
Managing IBS symptoms requires a combination of dietary adjustments, stress management techniques, and other lifestyle changes. The following tips have been proven to help ease the symptoms of IBS, allowing individuals to feel more comfortable and regain control of their digestive health.
1. Try the Low-FODMAP Diet
One of the most effective dietary strategies for managing IBS is following a low-FODMAP diet. FODMAPs are a group of short-chain carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine, leading to fermentation and bloating in the gut. These carbohydrates can be found in a variety of foods, including certain fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products, and sweeteners. The low-FODMAP diet involves limiting high-FODMAP foods and gradually reintroducing them to identify personal triggers. Some common high-FODMAP foods to avoid include garlic, onions, apples, dairy products (containing lactose), wheat, and certain legumes. By following this diet, many people with IBS experience a significant reduction in symptoms like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort.
2. Gradually Increase Fiber Intake
Fiber is essential for digestive health and can play a significant role in managing IBS. Soluble fiber, found in foods like oats, chia seeds, and psyllium, helps absorb water and form a gel-like substance in the intestines. This can help regulate bowel movements and reduce both diarrhea and constipation. However, it’s important to increase fiber intake gradually. Adding too much fiber too quickly can cause bloating, gas, and discomfort. Start by introducing fiber-rich foods slowly and pay attention to how your body responds. Soluble fiber can be particularly beneficial, while insoluble fiber (found in foods like whole wheat and some vegetables) may irritate your digestive tract if consumed in large amounts.
3. Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration is crucial for digestive health, especially for individuals experiencing diarrhea or constipation as part of their IBS. Drinking enough water helps your body break down food, absorb nutrients, and keep your digestive system running smoothly. It also helps with the passage of fiber through your digestive tract, which can help alleviate constipation. The general recommendation is to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water a day, but this amount may need to be increased depending on your individual needs. Be mindful of your caffeine and alcohol intake, as these can irritate your gut and exacerbate IBS symptoms. Instead of sugary or caffeinated beverages, opt for water, herbal teas, or electrolyte drinks to keep your body hydrated.
4. Incorporate Probiotics Into Your Diet
Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that can help support a healthy gut microbiome. Many people with IBS have an imbalance in their gut bacteria, which may contribute to digestive symptoms. Taking probiotics can help restore the balance of good bacteria in your gut, potentially alleviating symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Probiotics can be found in foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut. Additionally, probiotic supplements are widely available, but it’s essential to choose the right strains based on your specific symptoms. It’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best probiotic supplement for your condition.

5. Limit Trigger Foods
Many people with IBS find that certain foods trigger their symptoms. Identifying these trigger foods and avoiding them can help you manage your condition more effectively. Common trigger foods include fatty foods, spicy foods, artificial sweeteners, dairy products (for those who are lactose intolerant), and alcohol. Keeping a food diary can be an excellent way to track what you eat and how it affects your symptoms. By noting which foods cause flare-ups, you can make informed decisions about your diet and avoid the foods that worsen your condition.
Contact Us
While IBS can be a challenging condition to manage, there are many effective ways to ease its symptoms and improve your digestive health. By following a low-FODMAP diet, increasing fiber intake gradually, managing stress, staying hydrated, considering probiotics, and limiting trigger foods, you can take proactive steps to manage your symptoms and live a more comfortable life. It may take time to find the right combination of strategies that work for you, so be patient and track your progress. If your symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider who can help you develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. At Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando, our team is committed to helping patients find effective solutions for managing IBS and improving their digestive health. Schedule a consultation with us today to take the next step toward relief.