How Fast Does The Progression of Stomach Cancer Spread?
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a serious medical condition affecting the lining of the stomach. Arising from the cells that form the lining of the stomach wall, this cancer begins within the stomach lining and can spread to other parts of the body (metastasize) when not treated. Stomach cancer is a significant global health concern, with millions of people diagnosed each year. Our goal is to encourage early detection and empower informed decision-making for treatment.
Types and Stages of Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer can be classified into different types based on the cells it originates from. The most common type is adenocarcinoma, which accounts for most stomach cancer cases. Other less common types include lymphomas, gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), and carcinoid tumors. Each type has unique characteristics and requires specific treatment.
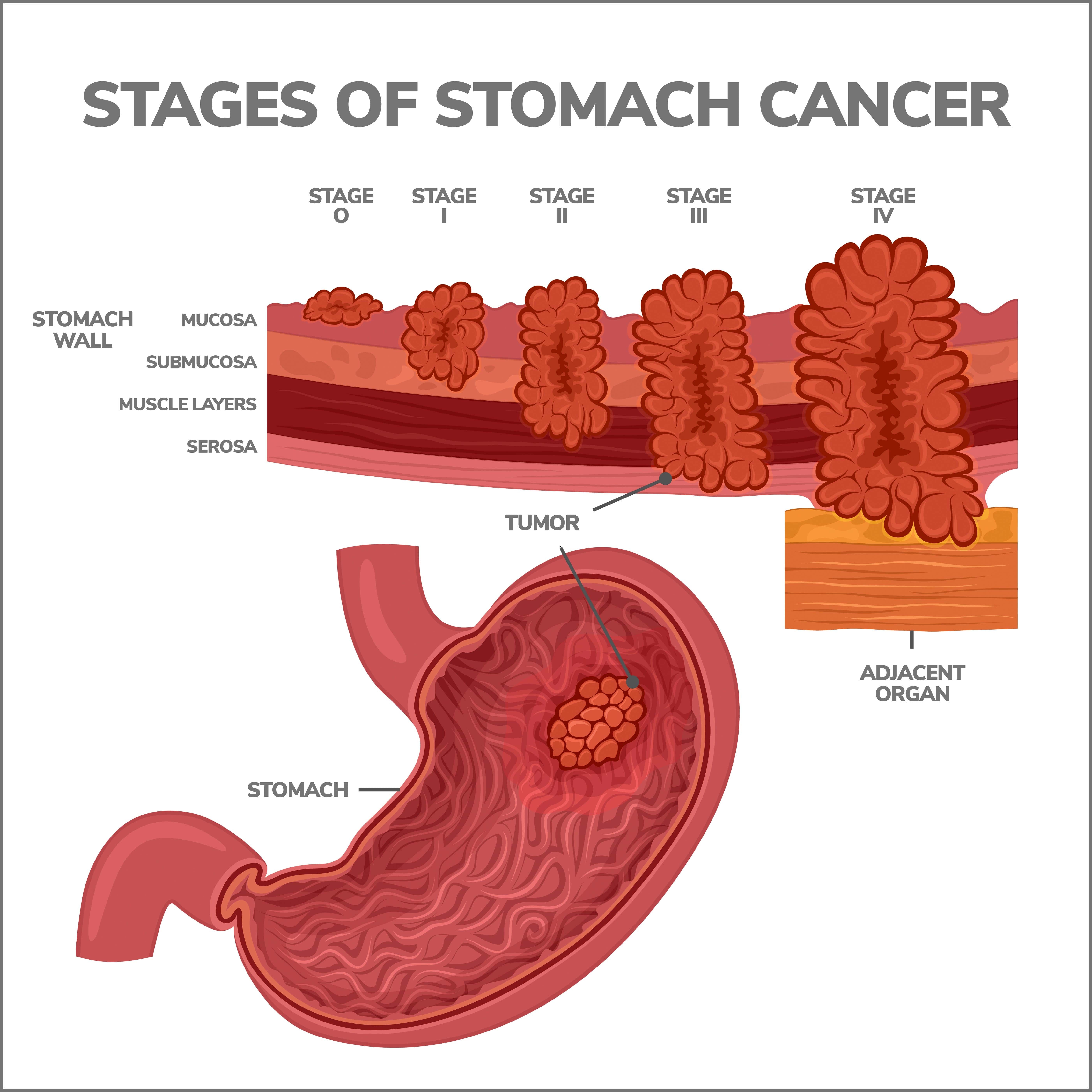
Stomach cancer is also categorized into different stages to determine the extent of its spread. The stages range from 0 to IV, with stage 0 being the earliest and stage IV being the most advanced. The staging helps healthcare professionals determine the appropriate treatment options and prognosis. It is crucial to detect stomach cancer early to increase the chances of successful treatment.
Factors that Contribute to the Spread of Stomach Cancer
Various elements contribute to the progression of stomach cancer. Among these, age stands out as a primary factor, as the risk of developing stomach cancer increases with age. Other risk factors include:
- A family history of stomach cancer.
- Certain inherited genetic conditions.
- Smoking.
- A diet high in smoked and salted foods.
- Chronic gastritis.
- A history of developing stomach polyps.
Besides these factors, certain infections, such as Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), have also been linked to an increased risk of developing stomach cancer. H. pylori is a bacterium that can cause chronic inflammation and ulcers in the stomach, potentially leading to the development of cancer over time.
Understanding the Progression of Stomach Cancer
The progression of stomach cancer refers to how the disease advances and spreads within the body. It typically begins in the stomach’s inner lining and gradually infiltrates the deeper layers of the stomach wall. As the cancer cells grow and multiply, they can invade nearby tissues, such as the lymph nodes, and eventually spread to distant organs, such as the liver, lungs, or bones. This process is known as metastasis.
The rate of progression can vary from person to person and depends on various factors, including the type and stage of stomach cancer, the individual’s overall health, and the effectiveness of the treatment received. Your gastroenterologist will monitor the progression of stomach cancer closely to adjust the treatment plan accordingly and provide the best possible care for the patient.
How Fast Does Stomach Cancer Spread?
The speed at which stomach cancer spreads can vary significantly. In some cases, the cancer may progress slowly over several years, while in others, it can spread rapidly within a shorter time frame. The rate of spread depends on various factors, including the aggressiveness of the cancer cells, the individual’s immune system response, and the effectiveness of treatment interventions.
Early detection plays a crucial role in determining the rate of spread. Regular screenings and prompt medical attention can help identify stomach cancer in its early stages, when it is more likely to be localized and easier to treat. Timely intervention can significantly slow down the progression of the disease and increase the chances of a successful outcome.
Symptoms and Warning Signs of Advanced Stomach Cancer
As stomach cancer progresses and spreads, it can cause a range of symptoms and warning signs. Common symptoms of advanced stomach cancer can include:
- Persistent abdominal pain or discomfort.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Loss of appetite.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Blood in the stool.
- Fatigue.
These symptoms can vary from person to person. They may also be present in other medical conditions, so it is best to consult with our GastroMD physicians for a proper diagnosis.

Diagnosing and Treating Stomach Cancer
Diagnosing stomach cancer involves a combination of a medical history review, physical examination, and various diagnostic tests. These tests may include:
- Imaging scans, such as CT scans or endoscopy.
- Tissue biopsy.
- Blood tests.
- Molecular testing to identify specific genetic mutations.
Once diagnosed, the treatment options for stomach cancer may include:
- Surgery.
- Chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy.
- Targeted therapy.
- A combination of these approaches.
Treatment choice depends on the stage and type of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and individual preferences.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes to Reduce the Risk of Stomach Cancer
While it may not be possible to avoid stomach cancer entirely, specific lifestyle changes and preventive measures can help reduce the risk. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Reducing the consumption of processed and smoked foods.
- Quitting smoking.
- Managing stress levels.
- Exercising regularly.
- Getting vaccinated against H. pylori infection if recommended by your physician.
- Regular check-ups and screenings are also essential, especially for individuals with a family history of stomach cancer or other risk factors.
Support and Resources for Stomach Cancer Patients
Stomach cancer can have a significant impact on the physical, emotional, and social well-being of patients and their loved ones. It is crucial to have access to support and resources that can provide guidance, information, and a sense of community. Various organizations and support groups offer resources, such as educational materials, counseling services, online forums, and financial assistance programs. These resources can help individuals navigate their journey with stomach cancer and provide them with the support they need.
Contact Us
Understanding stomach cancer progression is essential for early detection, proper diagnosis, and effective treatment. The speed at which stomach cancer spreads can vary, depending on various factors. Regular screenings, lifestyle modifications, and prompt medical attention play a crucial role in reducing the risk of stomach cancer and enhancing outcomes for patients.
If you or a loved one is navigating the complexities of stomach cancer, remember that you’re not alone. Take a proactive step in your health journey by contacting Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando for personalized guidance and unwavering support. Early detection can make a significant difference, so don’t hesitate to contact one of our gastroenterologists. Your well-being matters to us. Together, we can face and overcome the challenges posed by stomach cancer.