
Celiac Disease in Children: What Parents Should Know
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the digestive system. When a child with celiac disease eats gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye—the immune system reacts by damaging the small intestine. This reaction can interfere with nutrient absorption and lead to a range of health issues. Understanding how celiac disease develops, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to manage the condition are all essential steps for parents who want to support their child’s health and well-being.
What Is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is a chronic condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the small intestine after gluten consumption. This damage flattens tiny finger-like structures called villi, which are responsible for absorbing nutrients. Over time, this can lead to malnutrition and other complications. Celiac disease is different from gluten sensitivity or wheat allergies because it causes an actual autoimmune reaction rather than just intolerance or allergy symptoms.

Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of celiac disease is not fully understood, but genetics and environmental factors play important roles. Children with a family history of celiac disease, type 1 diabetes, or other autoimmune conditions are at higher risk. Certain genes, particularly HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8, are strongly associated with the condition, though having these genes does not guarantee a child will develop celiac disease. Celiac disease can develop at any age after gluten is introduced into the diet, and symptoms may appear gradually or suddenly, sometimes triggered by events such as infections, stress, or changes in diet. Early recognition of risk factors can help parents monitor for signs and seek timely medical evaluation.
Signs and Symptoms in Children
Symptoms of celiac disease vary widely and can affect more than just the digestive system. Common signs to watch for in children include:
- Digestive Symptoms: Chronic diarrhea, constipation, bloating, gas, abdominal pain, and nausea.
- Growth and Development Issues: Slow growth, delayed puberty, or short stature due to poor nutrient absorption.
- Behavioral and Emotional Symptoms: Irritability, mood changes, or difficulty concentrating, sometimes called “brain fog.”
- Other Symptoms: Fatigue, weight loss, skin rashes (such as dermatitis herpetiformis), and iron-deficiency anemia.
- Dental Problems: Enamel defects, frequent cavities, or delayed tooth development can sometimes appear in children with untreated celiac disease.
Because these symptoms can mimic other conditions, celiac disease is often overlooked or misdiagnosed. If your child shows persistent digestive issues or growth delays, it’s important to seek medical evaluation.
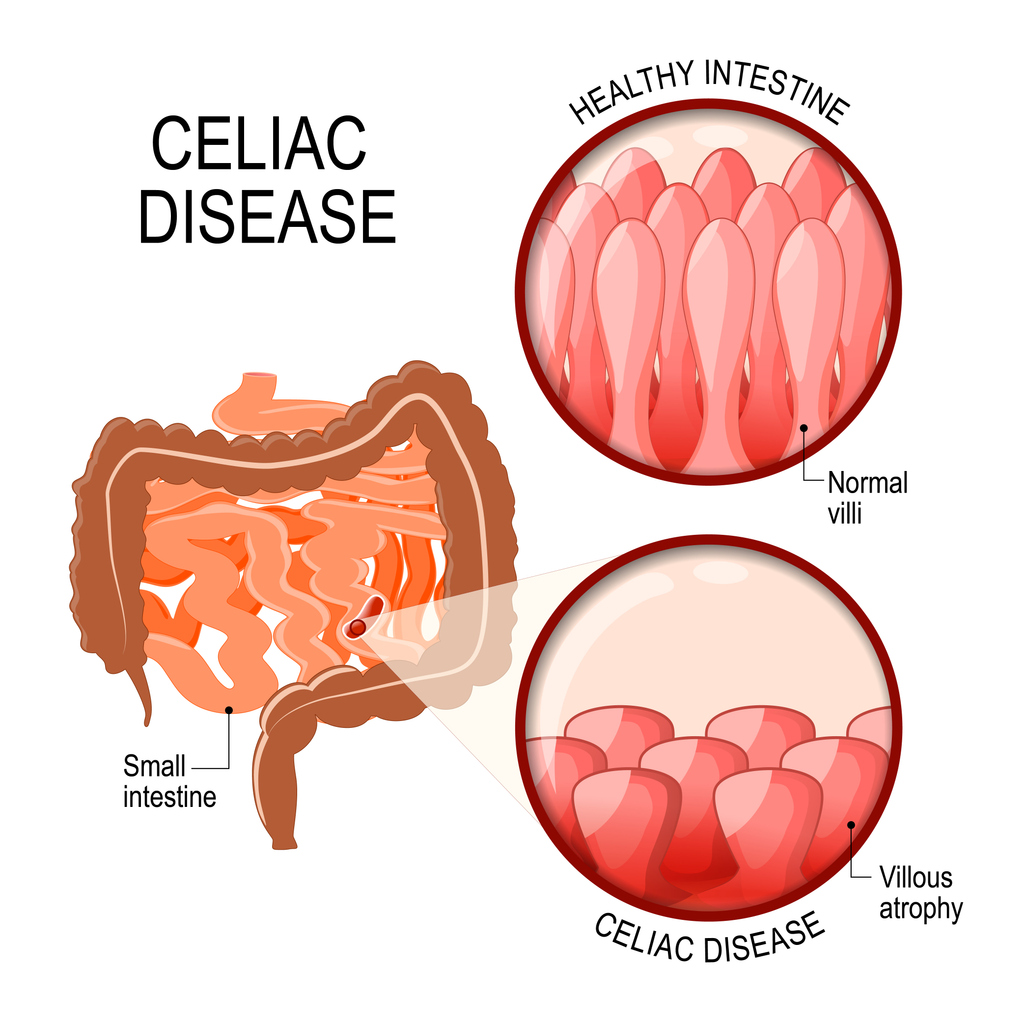
Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
Diagnosing celiac disease usually begins with blood tests to look for specific antibodies that suggest an immune reaction to gluten. If blood tests are positive, an upper endoscopy with a biopsy of the small intestine is typically performed to confirm the diagnosis and assess intestinal damage. It is important that your child continues eating gluten before and during testing—removing it too soon can lead to inaccurate results.
Managing Celiac Disease in Children
The only effective treatment for celiac disease is a lifelong gluten-free diet. This means avoiding all foods containing wheat, barley, and rye. With guidance from a doctor or dietitian, parents can help ensure that their child receives proper nutrition while staying gluten-free. Key steps include:
- Reading Food Labels: Gluten can hide in sauces, processed foods, and snacks. Always check ingredient lists carefully.
- Creating Safe Eating Habits: Educate your child about which foods are safe and which are not, especially at school or social events.
- Preventing Cross-Contamination: Use separate cooking utensils, toasters, and cutting boards to avoid contact with gluten-containing foods.
- Providing Balanced Nutrition: Work with a dietitian to ensure your child gets enough fiber, iron, calcium, and vitamins, which may be harder to obtain on a gluten-free diet.
- Planning Ahead for Meals and Snacks: Preparing gluten-free meals and snacks in advance can help reduce stress, prevent accidental gluten exposure, and make it easier for your child to enjoy safe options at school, parties, or while traveling.
Living with Celiac Disease: Support for Families
Adjusting to a gluten-free lifestyle can be challenging, especially for children. Parents can support their child by planning ahead for school lunches, communicating with teachers and caregivers, and encouraging open conversations about how the child feels. Many families find comfort in joining celiac support groups or connecting with others facing the same challenges. With proper care and support, children with celiac disease can thrive and enjoy a happy, healthy childhood.

When to Contact a Doctor
If your child experiences persistent digestive issues, unexplained fatigue, or signs of delayed growth, it is important to consult a healthcare provider as soon as possible. A doctor can order specific blood tests and, if needed, an intestinal biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of celiac disease. Early detection is key—starting treatment promptly can prevent serious complications such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, anemia, or delays in physical and cognitive development. It is important not to begin a gluten-free diet before testing, as removing gluten too early can interfere with accurate results and make diagnosis more difficult. With the right medical guidance, you can ensure your child receives proper care, nutritional support, and a safe plan for long-term management.
Contact Us
Celiac disease in children can be overwhelming, but with the right knowledge and support, it is manageable. Recognizing symptoms early, working with healthcare professionals, and maintaining a gluten-free lifestyle are key to helping your child stay healthy. At Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando, our specialists provide compassionate care and personalized treatment for children with celiac disease. We are here to guide your family every step of the way—from diagnosis to long-term management. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the next step toward protecting your child’s digestive health.