Parasitic Infections Condition
Many different issues can hurt your digestive system. One irritating and potentially serious problem is known as a parasitic infections condition.
Parasite Overview
Parasites are defined as tiny organisms that live inside a host. They survive by feeding off their host. Parasites found in the human digestive tract are typically found inside your intestines.
Intestinal Functions
Your intestines are comprised of the small and large intestines. The large intestine is also referred to as the colon.
These vital organs perform several necessary functions like:
- Processing the foods and drinks you consume.
- Absorbing nutrients from what you eat.
- Sorting out waste materials for elimination.
- Ensuring the proper flow of digestion.
When any of these actions do not run smoothly, your risk of developing a digestive system or systemic illness significantly increases.
How Parasites Enter Your Body?
Intestinal parasites have several entry methods into your body.
In many cases, these organisms live and breed in sources like water and soil. As a result, foods grown in the ground or items placed in contaminated water can become infected with parasites.
You can become infected through what doctors refer to as the “fecal-oral route.” Parasitic organisms or their eggs infiltrate the feces of a host animal that an unsuspecting person comes into contact with.
In many instances of human infection, people place their hands on extremely small amounts of feces discarded from a family pet or other animal. Then, without thinking, they consume tainted food or touch their mouths. This process provides the route for the parasite to enter your system.
Other possible means of infection include swimming in a pool or bathing in contaminated water.
Common Types of Intestinal Parasites
In most cases, a parasitic infections condition is most common in rural, underdeveloped, or developing regions or countries where sanitation is poor or where foods are not handled following strict safety standards.
These ailments can also occur in developed nations. Parasites common to the United States include:
- Giardia.
- Pinworm.
- Hookworm.
- Amebiasis.
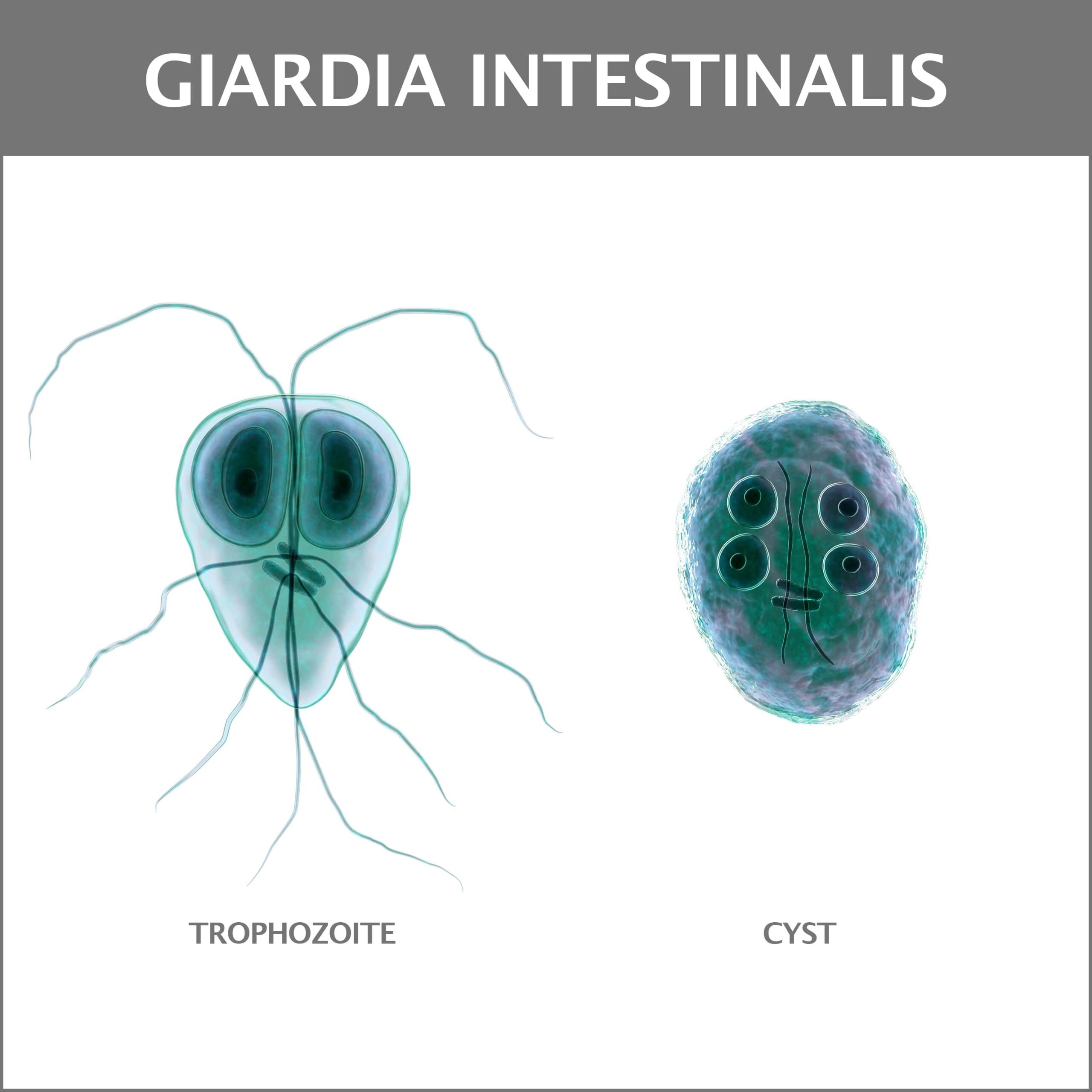
It is important to realize that there are countless numbers of species seen throughout the world and are far more common in places like Africa, Asia, and South America. If you have been traveling in these locations, you risk taking parasites back home with you.
Symptoms
The presence or severity of symptoms caused by intestinal parasites will vary depending on the specific type or species involved. Some common symptoms include:
- Abdominal cramping.
- Flatulence.
- A gas buildup.
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Greasy, smelly stools.
Lingering symptoms can result in dehydration and weight loss. Also, other organisms might cause nutritional deficiencies capable of weakening your immune system and leaving you susceptible to many minor and severe health disorders.
Complications
If left unaddressed for extended periods, parasitic infections in the intestines could lead to complications like intestinal obstructions and anemia. These problems are typically seen in older patients or people with compromised immune systems.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a parasitic infections condition can be challenging because their symptoms are also seen in other common problems.
If your doctor suspects that you might have some type of intestinal parasite, they may begin the diagnostic process by asking you:
- Have you traveled anywhere?
- What does your diet consist of?
- Have you been in contact with anyone from Africa, Asia, or South America?
Confirming a diagnosis usually requires the use of some diagnostic test. Some of these include:
- Blood Tests – Certain intestinal parasites can be identified through blood tests. Two types of blood tests can be used; a blood smear (which identifies parasites circulating through the bloodstream) or serology (which searches for antigens or antibodies produced by your immune system in your body’s quest to fend off the foreign intruders.)
- Fecal Examinations – Your doctor might take a stool sample and send it off to the lab. This examination is called an ova and parasite test. In some instances, the eggs and living parasites may be found in the fecal matter.
- Colonoscopy – A colonoscopy is performed using a small tube-like device known as a colonoscope. This apparatus is equipped with a camera capable of feeding internal images of your colon to a computer monitor. These live shots allow doctors to look directly into your colon and detect the presence of any parasites or many other issues capable of producing similar symptoms.
- Internal Imaging Devices – Occasionally, imaging apparatuses like MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or CT (computerized tomography) might detect a parasite’s presence or any other abnormalities.
Potential Treatment Options
The treatment chosen by your doctor will depend on several key issues, such as:
- Your age.
- General health.
- The specific type of parasite involved.
- The severity of the infestation.
Many prescription drugs are effective at eliminating these organisms. Researchers have also found that several natural remedies may help, but do not try them on your own without consulting your doctor:
- Papaya Seeds – A 2015 study was performed on schoolchildren from Kenya infected with roundworms. One group of children was given papaya seeds, while the other was given an anti-parasitic medication. The group that ingested the papaya seeds saw a 79 percent reduction in the presence of the parasite’s eggs in their digestive tracts versus the 64 percent decrease seen in those given the drugs.
- Wormwood – Studies have shown that extracts from the wormwood plant have effectively combated intestinal parasites such as tapeworms.
- Pumpkin Seeds – Pumpkin seeds contain large quantities of amino acids. These protein-like nutrients are said to have strong anti-parasitic properties.
- Dietary Adjustments – Doctors believe that positive outcomes may come from:
- Consuming foods high in beta carotene (like carrots, potatoes, and yams).
- Ingesting probiotic supplements.
- Increasing your intake of products containing Vitamins B and C.
- Upping your ingestion of garlic.
Physicians also recommend avoiding raw or not well-cooked meat or fish. You are also strongly encouraged to limit your alcohol, caffeine, refined grains, and sugar-laden products.
Staying hydrated keeps the digestive tract functioning properly and helps flush parasites out of your body.
Prognosis
Your chances of fully recovering are good if you are young, well-nourished, and do not have any significant underlying illnesses. It is hard to pinpoint specific time frames. Recovery periods will depend on the particular parasite involved and the treatment method used to treat it.
Prevention
You might decrease your risk of developing an intestinal parasite by practicing preventative measures including:
- Washing your hands after handling animals or pet waste.
- Cooking food at recommended temperatures and suggested preparation times.
- Trying to avoid swallowing water in pools, lakes, or streams.
- Being vigilant when visiting rural or developing places.
The most important thing is washing your hands frequently, especially after encountering commonly touched surfaces, pet waste, animals, or raw food.

Contacting Us
Our practice began more than 15 years ago and has emerged as one of the leading gastroenterology practices in central Florida. We perform several diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere. Patient care is always our top priority. Contact us today!