
A Lump in Your Throat Symptom
Every now and then, you may experience a seemingly alarming digestive tract symptom. One such condition is a lump in the throat.

Overview
Actually, a lump in the throat is medically classified as the globus sensation.
This physical condition is considered common, and you will likely experience it in short spurts on several occasions during your lifetime. Researchers have found that 46% of all Americans have felt a lump in their throats.
This symptom accounts for 4% of all doctor visits specializing in ear, nose, and throat disorders.
If you have encountered this problem, you know it feels like a frog lodged in your throat. The disorder is often uncomfortable and potentially embarrassing. Should it occur frequently or be accompanied by other notable symptoms, it may suggest a more serious medical condition.
Causes
A lump in the throat has many possible causes. Several are gastrointestinal disorders, including:
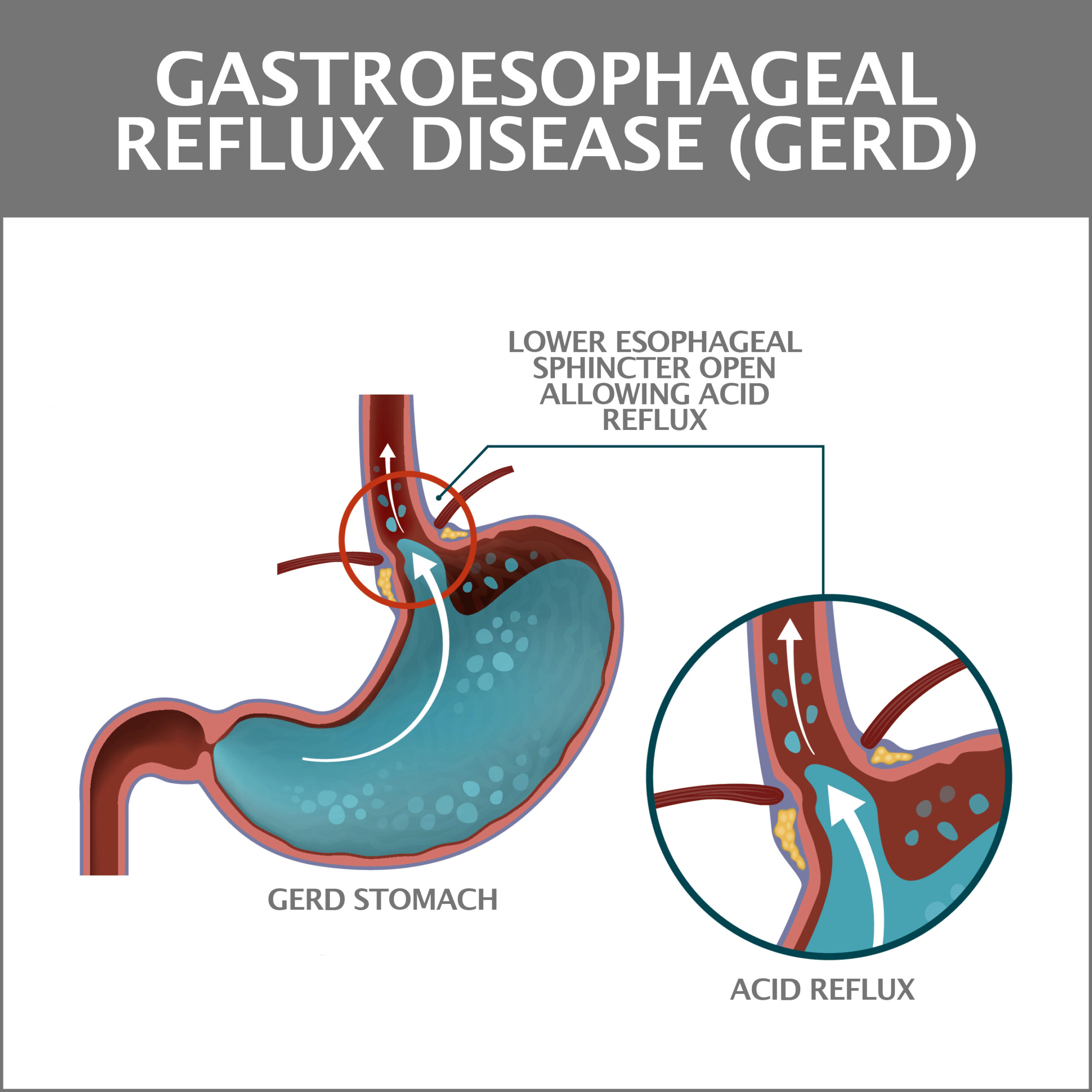
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease – Sometimes abbreviated simply as GERD, this happens when the upper esophageal sphincter does not correctly open and close. This enables stomach acid to creep into the esophagus carrying the potential to cause many unpleasant symptoms like the globus sensation.
- Esophageal Damage – Esophageal damage might also be to blame. One of the more common underlying factors leading to this problem is GERD. Corrosive acid causes a gradual deterioration of esophageal lining and tissues, which may lead to symptoms, including a lump in your throat.
- Undigested Food – Occasionally, the problem might result from undigested food getting stuck inside your esophagus. This may be because you ate too quickly or swallowed a large part of food without adequately chewing it.
Disorders Not Related to The Digestive System
A lump in the throat could also be caused by non-digestive tract conditions such as:
- Nasal and throat illnesses like tonsilitis, sinus infections, and allergies like hay fever.
- Stress.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Mouth and jaw disorders.
- The inability to produce enough saliva.

In rarer instances, the problem can result from benign and malignant tumors originating in the esophagus or other body parts.
Risk Factors
Your risk of experiencing a lump in the throat increases if you engage in digestive tract system-irritating activities such as:
- Consuming alcohol excessively.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco products.
- Eating a diet with spicy or overly processed foods.
Accompanying Symptoms
The specific symptoms you experience with the globus sensation can vary depending on the underlying cause. Physical symptoms may accompany the issue, including:
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Digestive concerns like gas, nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Swallowing difficulties.
- Neck and oral pain.
You might also have symptoms like fever, muscle aches, fatigue, decreased appetite, coughing, breathing trouble, and unintended weight loss.
Complications
Continual occurrences of the globus sensation can result in significant complications.
The issue may be indicative of a serious underlying illness like cancer. Even when not caused by a notable disease, a lump in the throat could render simple activities like eating and speaking challenging, resulting in several unpleasant physical and social complications.
When Should Medical Help Be Sought?
In many cases, a lump in the throat is not indicative of a significant medical problem and only lasts for a brief duration. You are encouraged to schedule a doctor visit if the problem persists, worsens, or is accompanied by any life-limiting issues.
Diagnosis
It is important to realize that the globus sensation is a symptom, not a complete disorder. Diagnosis will typically involve several stages.
During the first step, your doctor will likely ask you questions such as when the discomfort began, if it is accompanied by any other potentially concerning symptoms, or if you have been diagnosed with or have a family history of illnesses capable of causing the problem.
After this phase, your doctor will visually examine your mouth, neck, and throat to determine if any underlying abnormalities can be found. Throat examinations often use a small, camera-equipped tool.
If no visible abnormalities are discovered, the problem is probably related to a simple, easily resolvable problem. If your doctor identifies any suspicious findings, you may be asked to undergo further testing, such as swallowing time measurements, chest x-rays, capturing internal photos of the esophagus, and manometry, which gauges the amount of pressure within the esophagus.
Potential Treatment Options
Simple and uncomplicated cases usually do not need aggressive treatment. For example, those resulting from anxiety might be corrected by limiting external stressors or anxiety-relieving activities.
Treatment for more significant instances will depend on the specific precipitating cause.
Occurrences resulting from GERD can usually be resolved with acid-suppressing medications. Cases caused by specific medical conditions often need a solution to that issue. Therapy will depend on the disorder’s severity.
Prognosis
A significant percentage of instances occur due to minor and short-lived issues. A solution might take longer if the symptom results from an underlying illness.
Prevention
Cases not caused by underlying illness may be prevented or curtailed through efforts such as stress reduction, drinking alcohol in moderation, cessation of smoking or chewing tobacco products, and consuming a diet with limited amounts of spicy or processed foods.
Contact Us
Our practice began more than 15 years ago and has emerged as one of the leading gastroenterology practices in central Florida. We perform various diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere where patient care is always a top priority. Contact us today!