What is Esophagitis?
Esophagitis, the inflammation of the esophagus lining, is a condition that occurs when the esophageal tissue becomes irritated and swollen. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach, allowing the passage of food and liquids.
When the delicate lining of the esophagus is damaged, it can lead to discomfort, pain, and various complications. Several factors can contribute to this inflammation, including acid reflux, infection, and even certain medications. Here we’ll cover all you need to know about esophagitis and its treatment options.
Symptoms of Esophagitis
Esophagitis symptoms can range from mild to severe and may vary depending on the underlying cause of the inflammation.
Esophagitis symptoms can vary in intensity depending on the underlying cause, ranging from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
- Heartburn: This burning sensation in the chest, often accompanied by a sour taste in the mouth, is a typical sign of acid reflux-induced esophagitis. It can occur frequently and worsen when lying down or after eating certain foods or beverages.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): Inflammation and swelling of the esophagus can make swallowing painful or difficult, resulting in discomfort or a sensation of food being stuck in the throat.
- Pain when swallowing (odynophagia): Pain may occur when swallowing solid foods or even liquids, depending on the severity of the inflammation, and can be sharp or burning.
- Regurgitation: The return of food or stomach contents to the mouth can occur, especially when the inflammation is severe, causing a sour or bitter taste and potential damage to the esophagus from stomach acid.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms may be present, mainly if an infection causes esophagitis, and can contribute to discomfort and difficulty eating.
- Chest pain: This symptom can mimic the pain experienced during a heart attack and may be accompanied by shortness of breath. Seek medical attention if chest pain occurs to rule out more serious conditions.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss: Severe inflammation and difficulty swallowing can lead to reduced food intake and unintended weight loss. Malnutrition and dehydration can become concerns if the issue is not addressed.

If you experience persistent or severe symptoms of esophagitis, it is crucial to consult with a gastroenterologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications and promote healing of the esophageal tissue.
Diagnosis the Condition
Diagnosing esophagitis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and specialized tests to determine the cause of the inflammation. The diagnostic process may include:
- Medical history and physical examination: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, dietary habits, medications, and any history of acid reflux or gastrointestinal issues. A physical exam will check for any abnormalities.
- Upper endoscopy: During this procedure, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) is inserted through the mouth to examine the esophagus, stomach, and upper part of the small intestine. This allows your gastroenterologist to visualize the esophagus lining and identify signs of inflammation, infection, or other abnormalities.
- Biopsy: During an upper endoscopy, your gastroenterologist may take small tissue samples from the esophagus for further analysis. This can help identify the presence of infection. Your doctor may then prescribe antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal drugs.
- Esophageal pH monitoring: This test measures the acidity levels in the esophagus over a 24-hour period, which can help determine if acid reflux is the cause of the inflammation.
- Barium swallow: This X-ray test involves swallowing a liquid containing barium, which coats the esophagus and allows for more precise imaging of the esophageal lining.
How Can I Treat My Esophagitis?
Treatment for esophagitis depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. Common treatment options include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors may be prescribed to reduce stomach acid production and promote healing of the esophagus. If an infection is the cause, antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal drugs may be prescribed accordingly.
- Lifestyle changes: Modifying your diet, such as avoiding spicy or acidic foods, can help minimize esophagitis symptoms. Eating smaller meals and avoiding lying down for at least two hours after eating can also help prevent acid reflux. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and quitting smoking can improve esophageal health.
- Esophageal dilation: In cases where strictures (narrowing) of the esophagus have developed due to chronic inflammation, a procedure called esophageal dilation may be performed. During this procedure, a small balloon or dilator is inserted into the esophagus to gently stretch and widen the narrowed area, allowing easier swallowing.
- Surgery: In severe cases of esophagitis, surgery may be necessary when conservative treatments have not provided relief or complications arise.
Surgical options may be needed in some cases, and it’s best to consult your gastroenterologist. Here are some surgical options they may suggest:
- Fundoplication – reinforcing the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent acid reflux.
- Esophageal resection – a damaged part of the esophagus is removed.
- Esophageal stenting – placing a self-expanding stent to hold the esophagus open.
- Esophageal reconstruction – a new esophagus is created using a portion of the patient’s intestine or stomach.
- Perforation repair – to fix any holes in the esophagus.
Each surgical procedure carries risks and potential complications, but the benefits often outweigh the risks, particularly in severe cases that have not responded to other treatments.
Top Prevention Tips for Esophagitis
Preventing esophagitis often involves addressing the underlying causes of the condition. Here are some general tips for reducing the risk of esophagitis:
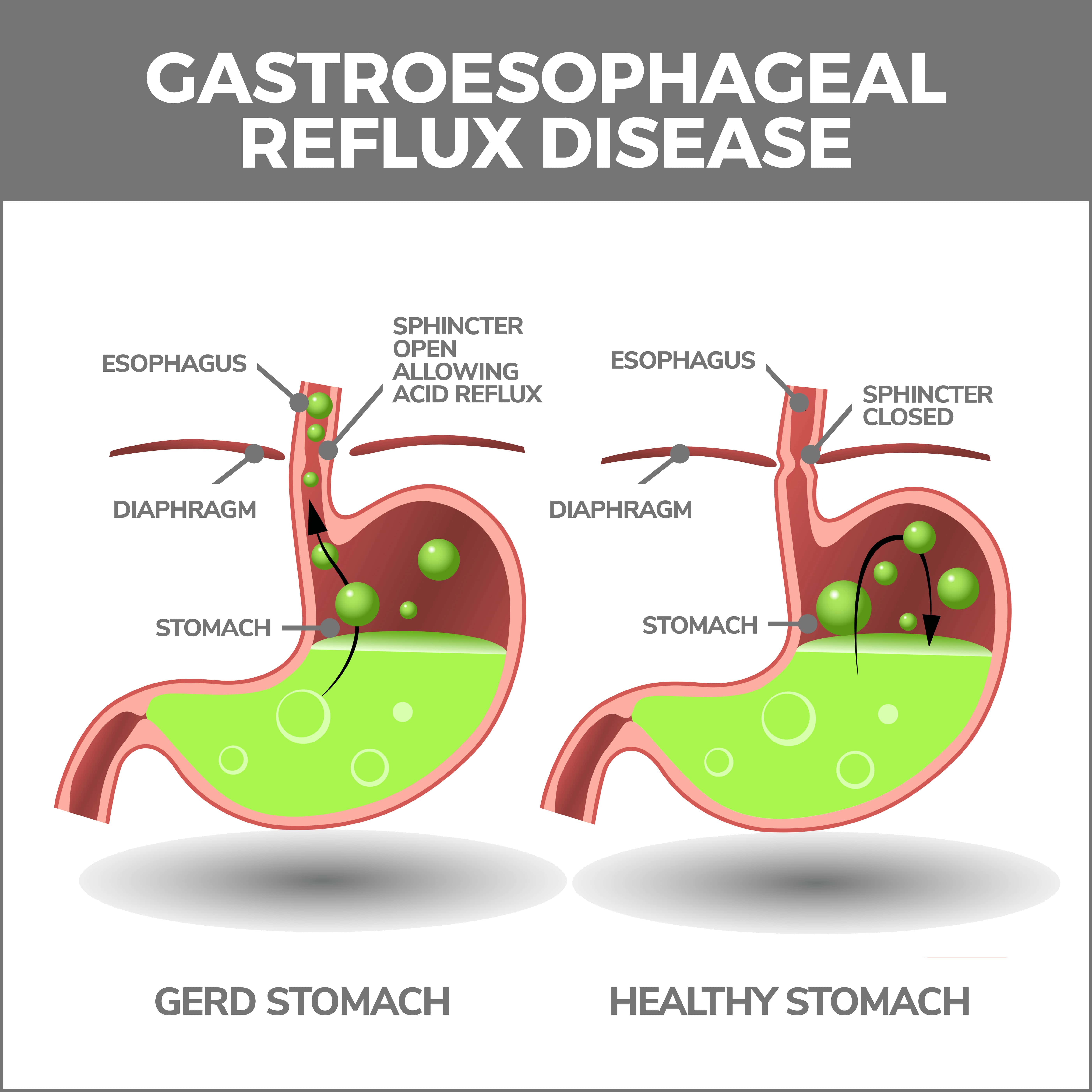
- Manage GERD: If you suffer from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), you can take steps to control it by avoiding trigger foods, eating smaller meals, not lying down immediately after eating, and elevating the head of your bed. Over-the-counter or prescription medications, such as antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors, may also help manage GERD symptoms and reduce the risk of esophagitis.
- Maintain proper medication use: Follow your doctor’s instructions when taking medications, especially those that can cause esophagitis. Swallow pills with plenty of water, avoid lying down immediately after taking medications, and never crush or chew medicines unless instructed to do so.
- Practice good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and avoid sharing utensils or drinks with others to reduce the risk of infections that can cause esophagitis.
- Treat allergies and asthma: Eosinophilic esophagitis can be triggered by allergies or asthma. Work with your doctor to identify and manage any allergies or asthma symptoms, including allergen avoidance or allergy medication use.
- Avoid irritants: Limit exposure to substances that can irritate the esophagus, such as tobacco smoke, excessive alcohol consumption, and very hot or spicy foods.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can contribute to GERD and increase the risk of esophagitis. A balanced diet and regular physical activity can help manage body weight and promote overall health.
- Seek medical attention: If you experience symptoms of esophagitis, consult a gastroenterologist for proper diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention can help prevent complications and promote healing.
Contact Us
If you’re experiencing symptoms of esophagitis, don’t hesitate to reach out to Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando. Our practice began more than 15 years ago and has emerged as one of the leading gastroenterology practices in central Florida. We perform a host of diagnostic procedures using state-of-the-art equipment in a friendly, comfortable, and inviting atmosphere where patient care is always a top priority. Contact us today!