
How to Recognize and Prevent Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a serious condition that can occur anywhere in the digestive tract, from the esophagus to the rectum. It can stem from a range of causes, from minor issues like hemorrhoids to more severe conditions such as ulcers or cancer. While GI bleeding is often a sign of an underlying health problem, recognizing the symptoms early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the different types of GI bleeding, along with their causes and risk factors, can help you take proactive steps to protect your digestive health.
What Is Gastrointestinal Bleeding?
Gastrointestinal bleeding refers to any blood loss in the digestive tract. It can occur in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine and may be mild or severe, depending on its cause and location. GI bleeding usually falls into two categories:
- Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding: Occurs in the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum (the first part of the small intestine).
- Lower Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding: Occurs in the jejunum and ileum (lower parts of the small intestine), large intestine, rectum, or anus.

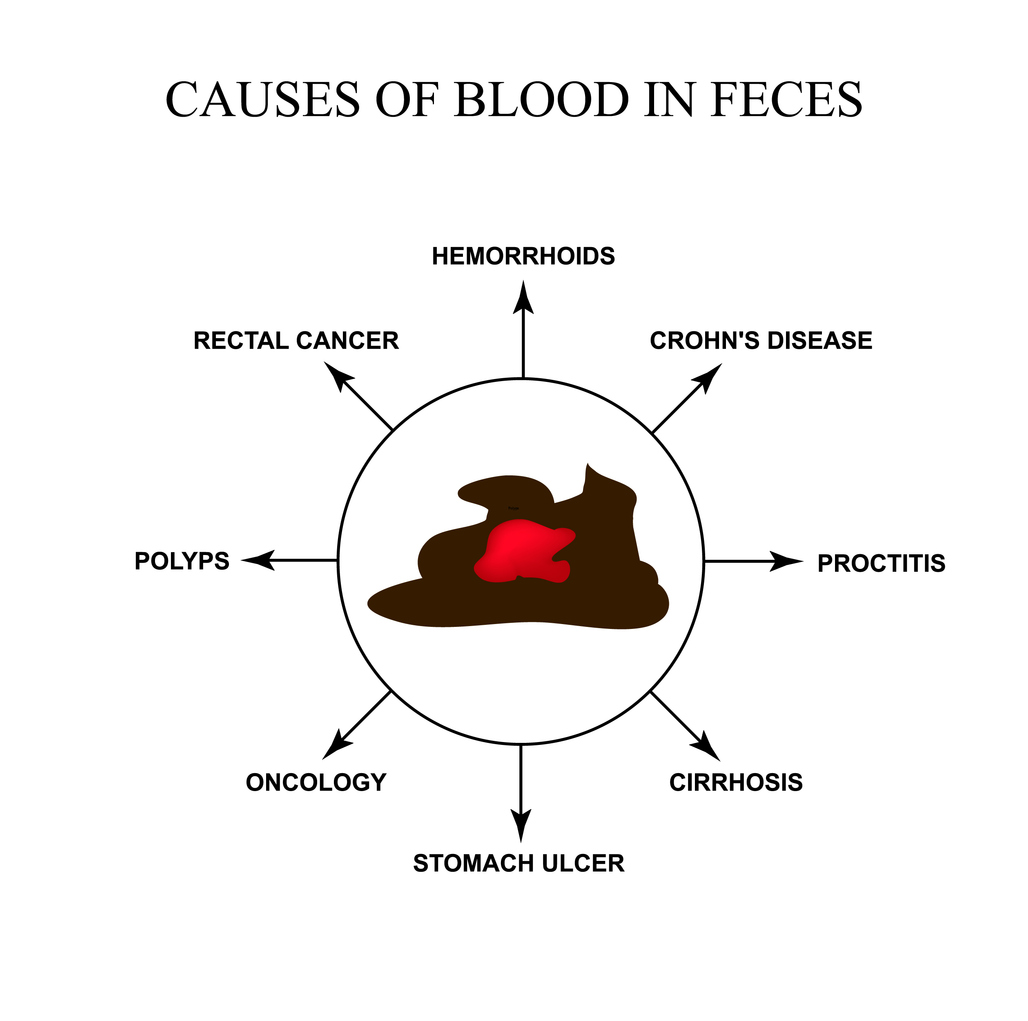
Common Causes of Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding
Gastrointestinal bleeding can result from various conditions, ranging from mild to serious. Common causes include:
- Peptic Ulcers: Sores on the stomach or small intestine lining, often caused by stomach acid or infections such as Helicobacter pylori.
- Diverticulosis: Small pouches in the colon that can become inflamed or infected, leading to bleeding.
- Hemorrhoids: Swollen veins in the rectum or anus that may bleed, especially during bowel movements.
- Colon Polyps or Cancer: Abnormal growths in the colon that may bleed, particularly if they are cancerous.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis can cause inflammation and bleeding in the digestive tract.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding
Symptoms vary depending on the location and severity of the bleeding. Common signs include:
- Visible Blood: Bright red blood in stool (hematochezia) or vomit (hematemesis) may indicate active bleeding.
- Dark, Tarry Stools: Black, tar-like stools (melena) suggest bleeding in the upper digestive tract.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Blood loss can lead to anemia, causing fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
- Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain may be linked to the underlying cause of the bleeding.
- Dizziness or Fainting: Severe blood loss can result in low blood pressure, leading to lightheadedness or fainting.
Diagnostic Tests for Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding
When gastrointestinal bleeding is suspected, several diagnostic tests may be performed to identify the cause and location. An endoscopy provides a detailed view of the upper digestive tract, while a colonoscopy allows examination of the large intestine and rectum. Blood tests may be ordered to check for anemia caused by blood loss. In certain cases, imaging tests such as computed tomography (CT) scans or angiography are used to locate bleeding within the digestive system. These diagnostic tools are essential for guiding treatment and ensuring effective management.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
- Age: People over 45 should begin regular screenings for colon cancer and other digestive issues, while those over 50 are at higher risk due to conditions like colon cancer or diverticulosis.
- Family history: Ulcers, colorectal cancer, or other gastrointestinal conditions can increase risk.
- Lifestyle choices: Excessive alcohol use, smoking, and poor diet can increase risk.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), blood thinners, and aspirin, can irritate the digestive tract and raise bleeding risk.
- Chronic conditions: Liver disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and peptic ulcers are contributing factors.
How to Prevent Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleeding
While not all causes of GI bleeding are preventable, you can reduce your risk with these steps:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced, fiber-rich diet supports digestion and lowers the risk of diverticulosis and hemorrhoids.
- Use Medications Wisely: Avoid excessive use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin. Ask your doctor about safer alternatives if needed.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: Too much alcohol can irritate the stomach lining and increase bleeding risk, especially with liver disease.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking raises stomach acid production and contributes to ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- Stay Up to Date on Screenings: Regular colon cancer and polyp screenings are especially important if you’re over 45 or have a family history of colon issues.

When to Seek Medical Help
It is important to seek emergency medical care if you experience symptoms that suggest significant bleeding. Signs such as persistent bright red blood in your stool, vomiting blood, black tarry stools, or severe abdominal pain should never be ignored. Dizziness, fainting, or feeling lightheaded may indicate serious blood loss and dangerously low blood pressure. Prompt medical attention is necessary to stop the bleeding, determine the cause, and provide the appropriate treatment. If you are concerned about your symptoms, do not hesitate to consult a doctor right away.
Contact Us
Gastrointestinal bleeding can be alarming, but understanding its causes and symptoms can make a big difference. Preventive measures, healthy habits, and timely screenings can all reduce the risk of serious complications. Paying attention to early warning signs and seeking care when needed helps ensure issues are treated before they become more severe. At Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando, our specialists provide comprehensive evaluations, advanced diagnostics, and personalized treatment plans. Whether you need preventive care, answers about symptoms, or guidance on long-term digestive wellness, we are here to help. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the next step toward protecting your well-being.