Colon and Rectal Polyps: What You Need to Know
Colon and rectal polyps are growths that develop on the inner lining of the large intestine or rectum. Many polyps are noncancerous (benign), while some can become cancerous over time. This underscores the importance of early detection and management. Understanding the causes of these growths, their diagnosis, and treatments can help you take steps to protect your digestive and overall health.

Understanding Colon Polyps
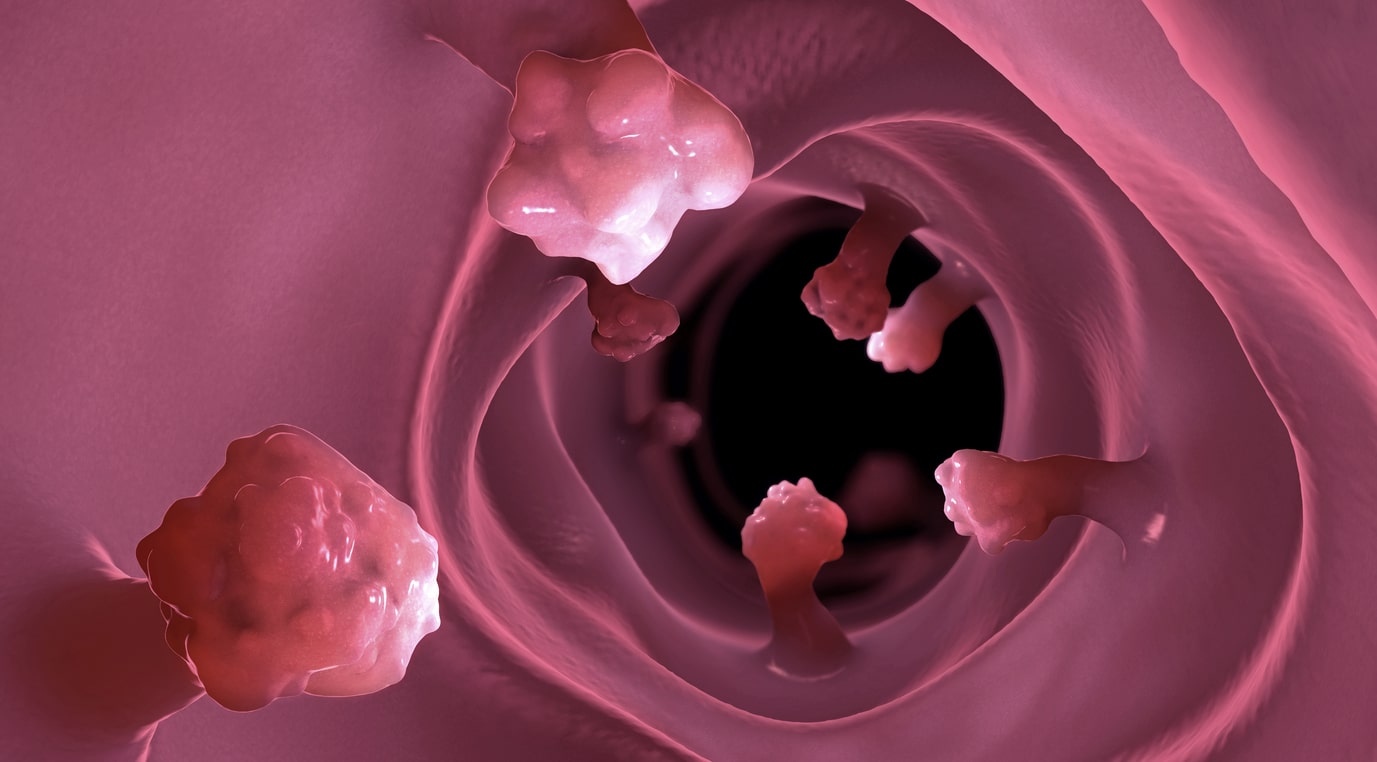
Colon polyps are abnormal tissue growths that can vary in size and shape. They can be as small as a pea or grow to several inches in diameter. An estimated 15% to 40% of adults may have polyps, with the likelihood increasing as individuals age. Polyps can be classified into two main types:
- Non-Neoplastic Polyps: These benign polyps include hyperplastic ones, which carry no cancer risk. They are small and generally do not require removal unless other concerns exist.
- Neoplastic Polyps: These polyps are precancerous. They can develop into cancer if untreated. There are two main types of Neoplastic polyps. Adenomas are the most common precancerous polyps. They can become cancerous over time. Sessile serrated polyps also have a cancer risk, depending on their size and location.
Symptoms of Colon Polyps
Colon polyps often develop without presentable symptoms, making regular screenings crucial for early detection. Some individuals may experience symptoms if the polyps are larger or if they lead to complications. Common symptoms can include:
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Diarrhea or constipation lasting more than a week may indicate larger polyps or cancer.
- Blood in Stool: The presence of blood, whether as red streaks or black stool, can be a sign of polyps or other gastrointestinal issues.
- Abdominal Pain: Large polyps can cause cramping or discomfort if they obstruct the bowel.
- Anemia: Chronic bleeding from polyps can lead to iron deficiency anemia, resulting in fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Sudden, unintentional weight loss may occur if larger polyps or related conditions affect the digestive system.
Risk Factors
Regardless of age or health status, anyone can develop colon and rectal polyps, but certain factors increase the risk. A family history of polyps or colorectal cancer significantly raises the risk, as does advancing age, especially after 50. Lifestyle choices also play a role. Smoking, heavy drinking, a diet high in red or processed meats, and lacking fiber can contribute to polyp formation.
Additionally, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes raise the risk. Being aware of these risk factors can help reduce your chances of developing polyps.
Importance of Screening
Screening for colon and rectal polyps is crucial for early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer, as many polyps develop without noticeable symptoms. Routine screenings offer numerous benefits, including identifying and removing polyps before they become cancerous, protecting digestive health, and catching issues early. Regular screenings are especially crucial for those with increased risk factors. These include a family history of colorectal cancer or polyps, advancing age, and some medical conditions. Colonoscopies can detect and remove polyps, greatly lowering the risk of progression.
Treatment Options
When colon and rectal polyps are found, various treatments can effectively remove them and prevent complications, including:
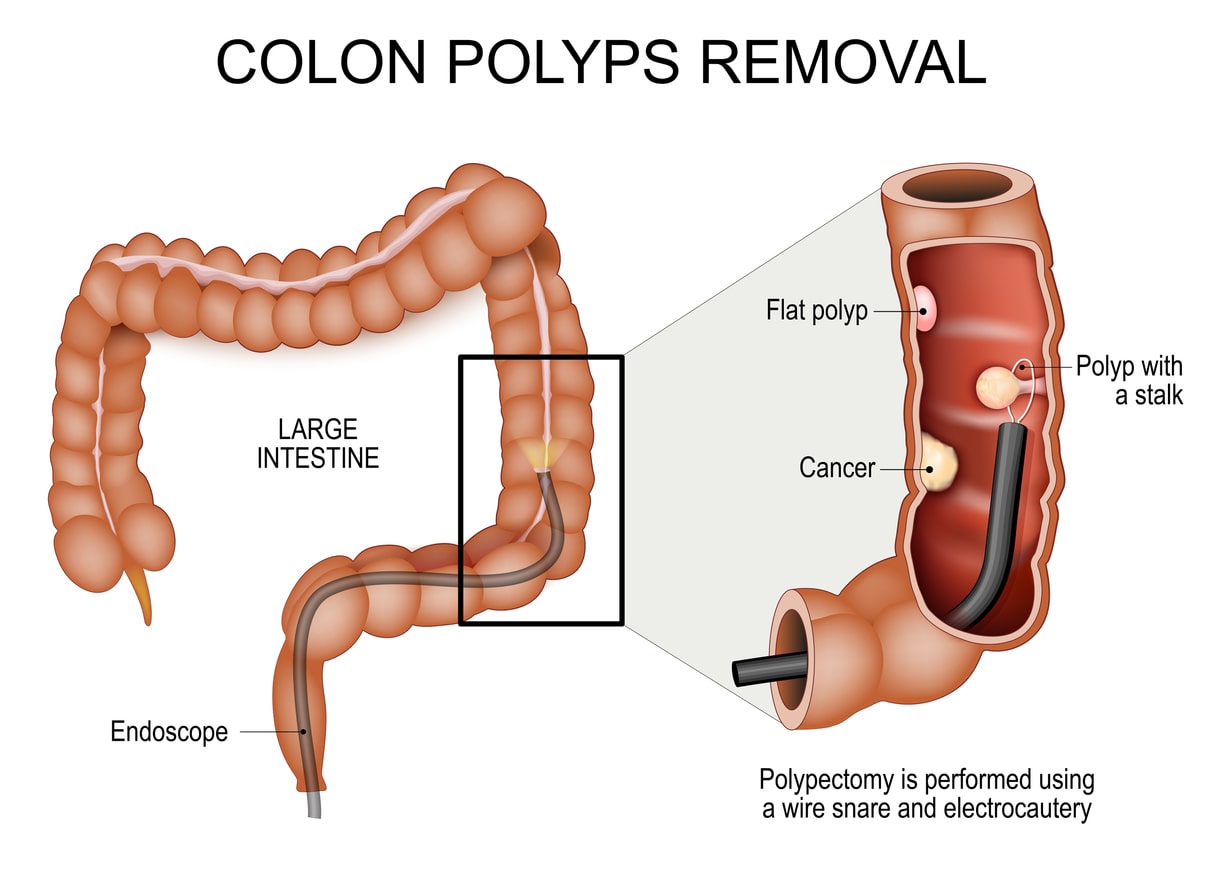
- Polypectomy: Polyps can often be removed during a colonoscopy using specialized tools.
- Surgical Removal: Larger or complex polyps may need surgery if they can’t be safely removed during a colonoscopy.
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: This method is used for larger polyps, where the polyp is removed through an endoscope.
- Laser Therapy: In some cases, polyps may be treated with laser therapy to shrink or remove them.
- Close Monitoring: After treatment, regular follow-up screenings are vital. They check for any recurrence of polyps.
Prevention Strategies
Preventive measures can greatly lower the risk of colon and rectal polyps. These include:
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber, while low in red or processed meats can lower the risk.
- Regular Exercise: Staying active helps maintain a healthy weight, which reduces the risk of polyps.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is linked to an increased risk of colorectal polyps, so quitting can lower your risk.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Reducing intake can lower the risk of polyps.
- Routine Screenings: Early detection through regular screenings, especially for those with risk factors, helps identify polyps before they become problematic.
When to Seek Medical Care
While many people may not experience noticeable symptoms from colon or rectal polyps, it’s still important to seek medical care if you have any concerns about your digestive health. If you have a family history of colorectal cancer or polyps, or if you’re over 50, regular screenings are recommended even in the absence of symptoms. These screenings can help detect polyps early before they cause problems.
If you’ve noticed changes in your digestive patterns or experience unexplained weight loss, persistent abdominal pain, or fatigue, these could indicate an underlying issue. It’s essential not to wait for more severe symptoms to appear—early intervention and regular screenings are vital for detecting polyps before they cause more serious health complications. Consulting a healthcare provider promptly is key to ensuring the best outcomes for your health.
Contact Us
If you’re concerned about your risk for colon or rectal polyps, or if you’re noticing any symptoms like changes in your bowel habits, don’t wait to get help. At Gastroenterology of Greater Orlando, we offer comprehensive screenings to check for any issues and provide personalized care to manage your digestive health. Our experienced team will guide you through your options, answer your questions, and make sure you are receiving the care you need.
Whether it’s for a routine check-up or if you have specific concerns, we’re ready to assist. Don’t wait for problems to become serious—taking action early can make a big difference in your health. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward safeguarding your digestive health for the future.